Create Role-bindings for a GitHub Team Using Terraform
There may be cases where an organization will want multiple users to have access to the same Chainguard organization. Chainguard allows you to grant other users access to Chainguard by generating an invite link or code.
In addition, you can now grant access to users using Terraform and identity providers like GitHub, GitLab, and Google. You can also manage access through these providers’ existing group structures, like GitHub Teams or GitLab Groups. Granting access through Terraform helps to reduce the risk of unwanted users gaining access to Chainguard.
This guide outlines one method of using Terraform to grant members of a GitHub team access to the resources managed by a Chainguard organization. It also highlights a few other Terraform configurations you can use to manage role-bindings in the Chainguard platform. Although this guide is specific to GitHub, the same approach can be used for other systems.
Prerequisites
To complete this guide, you will need the following.
terraforminstalled on your local machine. Terraform is an open-source Infrastructure as Code tool which this guide will use to create various cloud resources. Follow the official Terraform documentation for instructions on installing the tool.chainctl— the Chainguard command line interface tool — installed on your local machine. Follow our guide on How to Installchainctlto set this up.- Access to a GitHub team. If you’d like, you can create a new GitHub organization and team for testing purposes. Check out GitHub’s documentation for details on how to do this.
- A GitHub Personal Access Token, with a minimum of read.org access. Follow GitHub’s documentation on the subject to learn how to set one up. Additionally, you will need to configure SSO for your personal access token if required by your organization.
Setting up your Environment
There are a few things you must have in place in order to follow this guide. First, create a testing directory to hold the Terraform configuration and navigate into it.
mkdir ~/github-team && cd $_
This will help make it easier to clean up your system at the end of this guide.
Next, you’ll need to set up a few environment variables that the Terraform configuration in this guide assumes you will have in place.
Start by creating an environment variable named GITHUB_ORG that points to the name of your GitHub organization. Run the following command to create this variable, but be sure to replace <your GitHub organization> with actual name of your organization as it appears in URLs. For example, if your organization owns a repository at the URL htttps://github.com/orgName-example/repository-name, then the value you would pass here would be orgName-example.
export GITHUB_ORG=<your GitHub organization>
Next, create a variable named GITHUB_TEAM set to the slug of the GitHub team for which you want to create a set of role-bindings. The Terraform configuration will use this detail to find and retrieve information about your GitHub team.
If you aren’t sure of what your team’s slug is, you can find it with gh, the GitHub command line interface. You can use a command like the following to retrieve a list of all your organization’s teams.
gh api -H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" -H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" /orgs/$GITHUB_ORG/teams
Scroll through this command’s output to find the slug value for the team in question.
[
. . .
{
"name": "Team Name",
"id": 9999999,
"node_id": "T_kwDOBTYtm84AbTQX",
"slug": "team-slug",
. . .
},
. . .
]
With the team’s slug in hand, run the following command to create the GITHUB_TEAM environment variable.
export GITHUB_TEAM=<your GitHub team slug>
Following that, you will need to provide Terraform with your GitHub personal access token so it can access information related to your GitHub organization. Rather than hard coding your token into the Terraform configuration or having Terraform prompt you to enter it manually, you can create an environment variable named GITHUB_TOKEN which Terraform will automatically use. Create this variable with the following command.
export GITHUB_TOKEN=<your GitHub token>
Lastly, the Chainguard role-bindings that this guide’s Terraform configuration will create must all be tied to an organization. Create another variable named CHAINGUARD_ORG with the following command, replacing <UIDP of target Chainguard IAM organization> with the UIDP of the Chainguard IAM organization you want to tie the role-bindings to. You can find the UIDP for your Chainguard IAM organization by running chainctl iam organizations ls -o table.
export CHAINGUARD_ORG="<UIDP of target Chainguard IAM organization>"
Following that, you will have everything you need in place to set up the Terraform configuration.
Creating your Terraform Configuration
As mentioned previously, we will be using Terraform to create role-bindings for each user in a GitHub team, giving them access to resources associated with a given Chainguard organization. This guide outlines how to create two Terraform configuration files that, together, will produce a set of such role-bindings.
To help explain both files’ purposes, we will go over what they do and how to create each one individually.
main.tf
First, we will create a main.tf file which will set up the necessary Terraform providers.
This file will consist of the following lines.
terraform {
required_providers {
chainguard = {
source = "chainguard-dev/chainguard"
}
github = {
source = "integrations/github"
}
}
}
provider "github" {
owner = "$GITHUB_ORG"
}
The terraform block defines the sources for the chainguard and github providers.
The provider block sets up the github provider with one argument — owner — that points to the GITHUB_ORG variable you set previously.
Create the main.tf file with the following command.
cat <<EOF > main.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
chainguard = {
source = "chainguard-dev/chainguard"
}
github = {
source = "integrations/github"
}
}
}
provider "github" {
owner = "$GITHUB_ORG"
}
EOF
Next, you will create the other configuration file that will actually create the role-bindings for your GitHub team.
rolebindings.tf
The rolebindings.tf file will contain a few separate blocks that retrieve information about the GitHub team members and create Chainguard role-bindings for each one.
The first block creates a github_team data source named team.
data "github_team" "team" {
slug = "$GITHUB_TEAM"
}
Using the arguments you provided in the github provider block in main.tf, Terraform will search for any GitHub teams matching the slug specified within this block. If Terraform can find a team with a matching slug in the specified GitHub organization, then you will be able to pull more data about this team down from GitHub.
After the first block retrieves information about the team, we need to retrieve information about each member of the team in order to create an identity for each of them. To this end, the next block creates a github_user data source named team_members.
data "github_user" "team_members" {
for_each = toset(data.github_team.team.members)
username = each.key
}
Because, we want this source to represent every member of the team, this block starts with a for_each meta-argument which accepts a toset map of the GitHub team members derived from the github_team source created previously.
Additionally, the github_user data source requires you to set the username argument to whichever user you want the data source to represent. In the Terraform Language, each.key is the map key corresponding to the objects referenced in the for_each argument. In this case, it means the username variable will be tied to a mapping of each member of the GitHub team within this Terraform configuration.
The next block retrieves Chainguard identities for each member of the GitHub team.
data "chainguard_identity" "team_ids" {
for_each = toset([for x in data.github_user.team_members : x.id])
issuer = "https://auth.chainguard.dev/"
subject = "github|${each.key}"
}
This block’s for_each meta-argument iterates through each member of the team. For each iteration, it retrieves that user’s GitHub ID and then retrieves a Chainguard identity that it derives using that GitHub ID.
If there are members of the GitHub team who have not yet registered with Chainguard, this method will still assign them the correct permissions when they log in for the first time.
The next block retrieves the predefined viewer role from Chainguard.
data "chainguard_role" "viewer" {
name = "viewer"
}
The final block puts all this information together to create the role-bindings for each member of the team.
resource "chainguard_rolebinding" "cg-binding" {
for_each = data.chainguard_identity.team_ids
identity = each.value.id
group = "$CHAINGUARD_ORG"
role = data.chainguard_role.viewer.items[0].id
}
This resource block iterates through the list of Chainguard identities, assigns each one to the IAM organization specified by the group argument, and binds each identity to the viewer role. Here, the group argument is set to the CHAINGUARD_ORG variable you created at the start of this guide.
Create the rolebindings.tf file with the following command.
cat <<EOF > rolebindings.tf
data "github_team" "team" {
slug = "$GITHUB_TEAM"
}
data "github_user" "team_members" {
for_each = toset(data.github_team.team.members)
username = each.key
}
data "chainguard_identity" "team_ids" {
for_each = toset([for x in data.github_user.team_members : x.id])
issuer = "https://auth.chainguard.dev/"
subject = "github|\${each.key}"
}
data "chainguard_role" "viewer" {
name = "viewer"
}
resource "chainguard_rolebinding" "cg-binding" {
for_each = data.chainguard_identity.team_ids
identity = each.value.id
group = "$CHAINGUARD_ORG"
role = data.chainguard_role.viewer.items[0].id
}
EOF
Note that the fourteenth line of this file contains a backslash (\).
subject = "github|\${each.key}"
This is an escape character which will prevent the dollar sign in that line from causing a bad substitution error.
Now that your Terraform configuration is in place, you’re ready to apply it and create role-bindings for each member of your GitHub team.
Applying your Terraform Configuration
First, run terraform init to initialize Terraform’s working directory.
terraform init
Then run terraform plan. This will produce a speculative execution plan that outlines what steps Terraform will take to create the resources defined in the files you set up in the last section.
terraform plan
If the plan worked successfully and you’re satisfied that it will produce the resources you expect, you can apply it.
terraform apply
Before going through with applying the Terraform configuration, this command will prompt you to confirm that you want it to do so. Enter yes to apply the configuration.
. . .
Plan: 2 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value:
After pressing ENTER, the command will complete.
. . .
Apply complete! Resources: 2 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Following this, any members of your GitHub team for whom you’ve created role-bindings will be able to view the resources associated with the Chainguard organization you specified. To do so, they need to log in to the Chainguard platform, either by logging into the Chainguard Console or with the following command.
chainctl auth login
After navigating to the Console or running the login command, they will be presented with the following login flow.
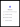
There, they must click the Continue with GitHub button to continue logging in under their GitHub account. Chainguard will immediately recognize their GitHub account because it is tied to the role-binding you created in the previous step, and they will be able to view the resources associated with the Chainguard organization specified in your Terraform configuration.
Optional Configurations
The Terraform configuration used in this guide is meant to serve as a starting point, and we encourage you to tweak and expand on it to suit your organization’s needs. This section contains a few alternative configurations that you may find useful.
For example, rather than applying the viewer role to your team’s role-bindings, you can apply one of the other built-in roles, or any custom roles created within your Chainguard organization. The following data and resource block examples could be used in place of the ones used in this guide’s rolebindings.tf file. Instead of granting the identities the viewer role, this grants them the editor role.
data "chainguard_roles" "editor" {
name = "editor"
}
resource "chainguard_rolebinding" "cg-binding" {
for_each = toset(data.chainguard_identity.team_ids)
identity = each.value.id
group = "$CHAINGUARD_ORG"
role = data.chainguard_roles.editor.items[0].id
}
The Terraform configuration language is quite flexible. You can update your Terraform configuration to retrieve information about a single user, rather than an entire team.
data "github_user" "user" {
username = "$USERNAME"
}
Likewise, you can retrieve a GitHub user’s Chainguard identity without having to include the for_each meta-argument.
data "chainguard_identity" "gh-user-chainguard-rb" {
issuer = "https://auth.chainguard.dev/"
subject = "github|${data.github_user.$USERNAME.id}"
}
You can refer to the Terraform language documentation for more information on extending the configuration outlined in this guide to suit your own needs.
Removing Sample Resources
To remove the resources Terraform created, you can run the terraform destroy command.
terraform destroy
This will destroy the Chainguard role-bindings created for your GitHub team. You can then remove the working directory to clean up your system.
rm -r ~/github-team/
Following that, all of the example resources created in this guide will be removed from your system.
Learn More
The procedure outlined in this tutorial can be tweaked to work with other identity providers, including Google and GitLab.
Last updated: 2024-05-09 08:48

